
Knee Replacement, Or Knee Arthroplasty, Is A Surgical Procedure To Replace A Damaged Knee Joint With An Artificial One. This Is Typically Recommended For Patients With Severe Arthritis, Primarily Osteoarthritis, When Conservative Treatments Have Failed To Provide Adequate Relief.
The Decision To Undergo Knee Replacement Is Made In Conjunction With An Orthopedic Surgeon. Common Indications For The Procedure Include Intractable Knee Pain Significantly Impacting Daily Life And Sleep. Severe Limitation Of Motion, Hindering Activities Of Daily Living. Joint Deformity Affecting Alignment And Function. Inability To Bear Weight On The Affected Knee.
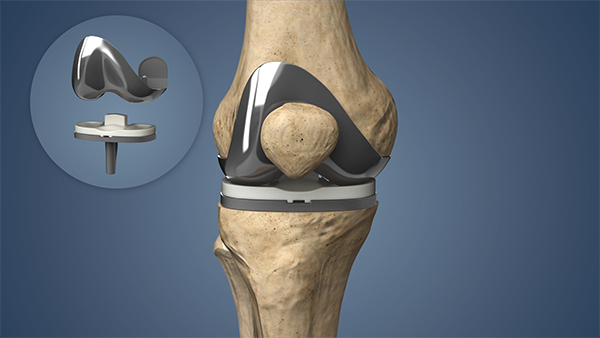
During Knee Replacement Surgery, Damaged Cartilage And Bone Are Removed, And Artificial Components Are Implanted. The Procedure Is Typically Performed Under General Anesthesia And Takes Approximately One To Two Hours. The Artificial Joint Is Designed To Replicate The Natural Movement Of The Knee, Restoring Function And Range Of Motion.
Post-Operative Recovery Involves Physical Therapy To Strengthen The Knee And Improve Flexibility. Patients Typically Begin Walking With Assistive Devices Shortly After Surgery, Gradually Progressing To Independent Ambulation. While Full Recovery May Take Several Months, Most Patients Experience Substantial Pain Relief And Improved Function Within Weeks.
Knee Replacement Surgery Offers Several Potential Benefits, Including: Significant Reduction In Knee Pain.Improved Ability To Perform Daily Activities.Enhanced Knee Stability And Strength.Increased Independence And Quality Of Life.It Is Important To Note That Individual Results May Vary. Factors Such As Overall Health, Age, And The Severity Of Arthritis Can Influence Outcomes.Disclaimer: This Information Is Intended For General Knowledge And Informational Purposes Only And Does Not Constitute Medical Advice. Patients Should Consult With A Qualified Healthcare Professional For Diagnosis And Treatment Of Any Medical Condition.